AIR COOLED CONDENSERS
Air cooled condensers are used in equipment for refrigeration, air conditioning and industrial processes. Thanks to the innovations developed, patented and tested by LU-VE, the air cooled condensers produced by the company:
• are economical to run
• function efficiently in all environmental conditions.
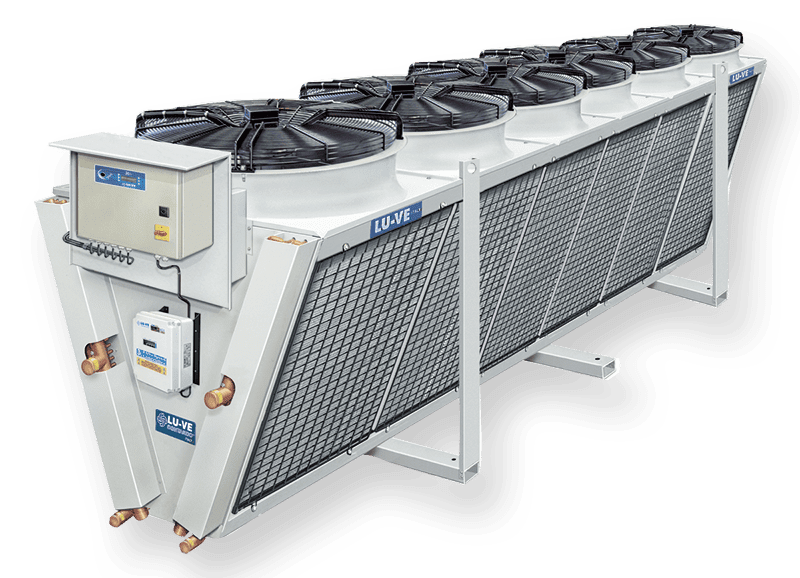
Air cooled condenser EHVD with double fan-row V-coil
- Maximum height 2500 mm: high capacity in restricted space
- 112 models from 164 to 2340 kW, double exchanger coil
- From 4 to 18 fans, Ø 800 – 900 mm
- Low noise operation (from 31 dBA) and reduced energy consumption
Main features Air cooled condenser EHVD with double fan-row V-coil
TURBOCOIL® heat exchanger
The extraordinarily efficient performance of the heat exchanger is due to the optimum combination of special profile aluminium fins and internally helically-grooved tubes.
- Turbocoil
- Steel Protected
- Safe Tubes System
- Turbofin
- SMART

Air cooled condensers XDHV with single fan-row V-coil
- Maximum height 1660 mm: high capacity in restricted space
- 126 models from 41 to 1000 kW, double exchanger coil from 1 to 8 fans, Ø 800 – 900 mm
- Low noise operation and reduced energy consumption
Main features Air cooled condensers XDHV with single fan-row V-coil
TURBOCOIL® heat exchanger
The extraordinarily efficient performance of the heat exchanger is due to the optimum combination of special profile aluminium fins and internally helically-grooved tubes.
- Turbocoil
- Steel Protected
- Safetubes Systems
- SMART
- Turbofin
Main features
10 different ranges for every installation requirement.
SUB 350 4-6 P
dBA 30÷49
From 1 to 4 fans Ø 350
230 V 1 ~ 50
SUB 500 SAV 4-6-8 P
dBA 30÷52
From 1 to 3 fans Ø 500
400 V 3 ~ 50 or 230 v 1 ~ 50
SUB 630 EAV 4-6-8P
dBA 42÷56
From 1 to 5 fans Ø 630
400 V 3 ~ 50
Operating principles
The fluid refrigerant at the outlet of a condenser is usually collected in a liquid receiving tank, in which the liquid and vapour phases coexist. The temperature of the condensate at the outlet of the liquid receiving tank is therefore at a temperature which coincides with the condensation temperature, excluding the effects induced by the pressure drop which the refrigerant undergoes while passing through the condenser.
.gif)
Advantages of subcooling
Subcooling the liquid condensate before expanding it and running it to the evaporator enables increased refrigerating power and increased energy efficiency to be achieved. All the heat given up to the environment during the subcooling phase is reintroduced into the refrigeration cycle as useful work (free, from the point of view of energy consumption) in the evaporation phase. An additional advantage of subcooling is the possibility of permitting pressure drops in the line which takes the refrigerant from the condenser to the expansion valve without the formation of vapours.